China’s factory cannot increase production, but if it receives subsidies, it will be limited for 10 years
It cannot increase wafer input by more than 5%.System semiconductor regulations were classified into high-tech products under 28 nanometers. Taiwan’s TSMC is also likely to be hit.What procedures are left?
Opinions from each company will be collected for 60 days and the extension of equipment export permits will remain variables.
On the 21st (local time), the U.S. Department of Commerce announced the details of the “guard rail” that restricts investment in China if it receives subsidies from the Semiconductor Support Act (CHIPS Act). The first document announced by the Ministry of Commerce on its website earlier in the day was 48 pages, but it was reduced to 44 pages. Just as the amount of documents went back and forth, there was also a lot of confusion over the interpretation of the guardrail.
Is it possible for Korean semiconductor companies that receive U.S. subsidies to make new investments in China?
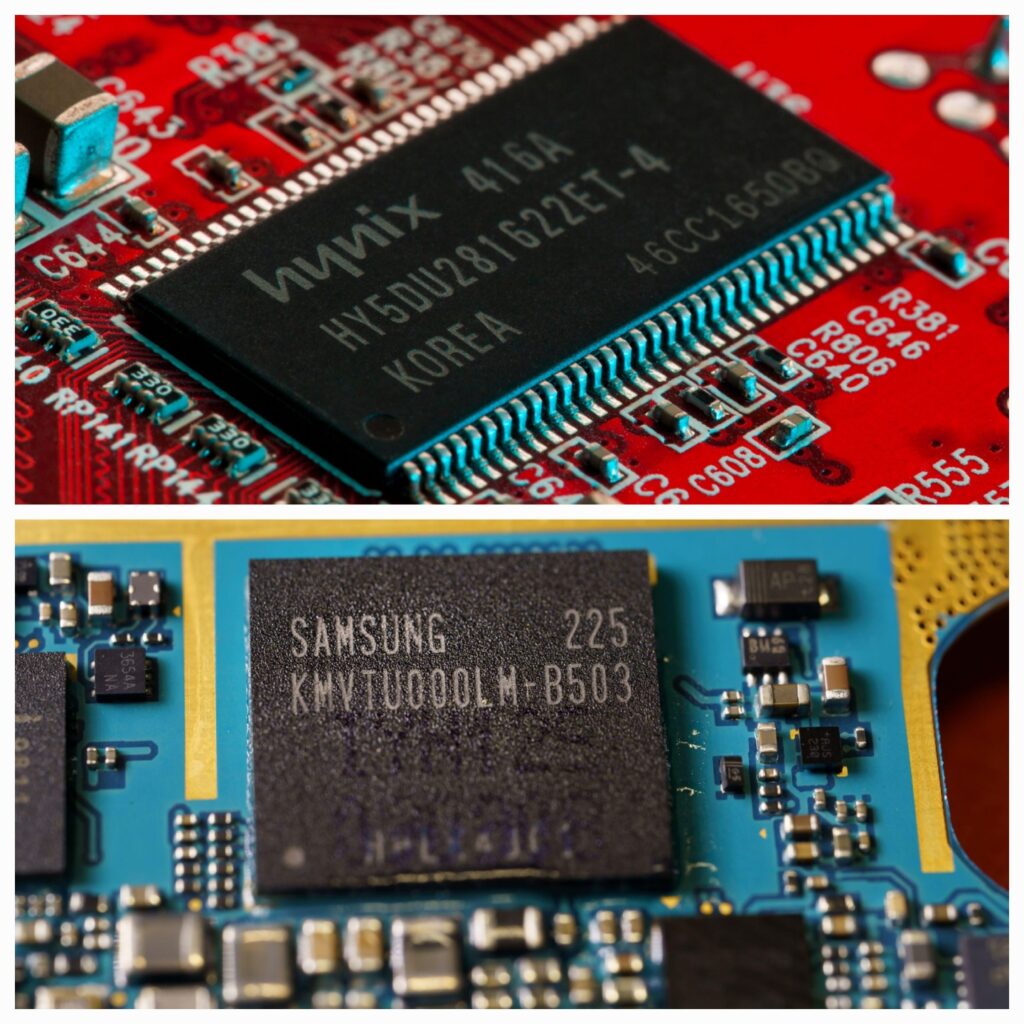
That’s virtually impossible. The Ministry of Commerce allowed the establishment of production lines only for general-purpose (legacy) semiconductors, which account for more than 85% of consumption in China. Semiconductors are exported from China. Allowing new investments in semiconductors could increase the global market’s dependence on Chinese production. For this reason, it is possible to make new investments only in semiconductors for domestic consumption in China. Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix mainly produce high-tech semiconductors in China. The share of consumption in China is also less than 85%. In other words, it is impossible to make new investments in China.
What about high-tech semiconductors and general-purpose standards?
Under the Semiconductor Support Act, general-purpose semiconductors are redefined every two years. Products that China can produce are classified as general-purpose semiconductors, and the rest as high-tech semiconductors. Currently, NAND flash with 128 layers or less, DRAM with 18 nanometers or more (nm, 1nm = 1 billionth of a meter), and system semiconductors with 28 nanometers or more are defined as general-purpose semiconductors. It was different when the Commerce Department announced a ban on semiconductor equipment exports in October last year. Although NAND and DRAM have the same definition of general-purpose semiconductors, the range of general-purpose system semiconductors is set to be 14 nano or 16 nano (pin-pet structure). This time, in the same way as the Semiconductor Support Act, more than 28 nanometers were designated as general-purpose system semiconductors.
It is interpreted as unfavorable to TSMC What is this like?
If 28 nanometers or more are selected as general-purpose system semiconductors, not 14 nanometers or 16 nanometers, the scope of guardrails will be expanded. However, TSMC is the only candidate company that produces system semiconductors in China to receive U.S. semiconductor subsidies. Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix are producing only NAND and DRAM in China.
Can Korean companies increase production in China?(Samsung and SK Hynix)
If a U.S. semiconductor subsidy is received, the expansion of semiconductors in China will be restricted for the next 10 years. The amount of wafer input, which is a disk that makes semiconductors, is the standard. If U.S. subsidies are received from the high-tech semiconductor sector, which is a major product of Korean companies, it can increase wafer input by up to 5 percent in China over 10 years. General purpose semiconductors can be increased by 10% over 10 years. In the case of Samsung Electronics’ NAND flash plant in Xi’an, China, wafer input has increased by 108% over the past 10 years. Allowing the expansion of “5%” is actually not to be newly expanded.
It is said that there is no limit to increasing production due to technological improvement, so what is this?
Through micro-process technology, the number of semiconductors produced per wafer can be increased by increasing the degree of integration. For this reason, Minister of Trade, Industry and Energy Lee Chang-yang also praised on the 22nd, saying, “The basic requirements for Korean companies to be relieved have been met.” Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix have mixed evaluations that “the worst has been avoided” and concerns that “it is difficult to continue its Chinese business in the mid- to long-term due to blocked new investment and limited production.”
What are the remaining procedures and variables?
Collect opinions for 60 days and receive applications for subsidies. In the second half of this year, each company that receives subsidies will sign an agreement with the Ministry of Commerce. At this time, depending on the negotiations, the contents of the agreement by company may be completely different. Apart from Guardrail, global semiconductor companies, including South Korea, are subject to U.S. export controls on semiconductor equipment to China. The South Korean chipmaker was suspended for a year in October last year. The South Korean government and businesses expect the grace period to be extended, but it remains to be seen whether it will take place.
KS CHOI
US ASIA JOURNAL



